|
TriTrack Guideway Grid
How the Guideway Grid Works:
The Quick Answer:
A computer advises the driver of the best path to take, and the driver then
decides whether to follow that route or not. The only merging is on the
ground, and you have to come down to the ground to make turns.
The Detailed Answer
Grid Layout
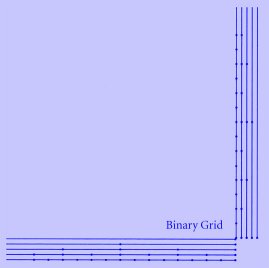 Each blue line on the map represents several lanes
of TriTrack guideway. There are lanes for each direction, and multiple lanes
in each direction. TriTrack cars only get on a
guideway at the beginning and only get off at the end. Once on, there is
no merging, there are no exits, and there are no turns.
Each blue line on the map represents several lanes
of TriTrack guideway. There are lanes for each direction, and multiple lanes
in each direction. TriTrack cars only get on a
guideway at the beginning and only get off at the end. Once on, there is
no merging, there are no exits, and there are no turns.
To get where you want to go, the lanes are made up of sections of guideway that
are each different lengths. One lane will be the 'short' lane, with guideway
hops that are only about 1-2 miles long. Another lane will be a 'medium' lane,
and there will be a 'long' lane that goes from the center of town non-stop to
the edge of town.
To make a turn, you hop down off the end of your guideway, then hop up on the
adjacent guideway going in the new direction.
Why?
By making each track one way only and eliminating merges, the system is kept
very simple and safety is greatly increased.
Getting Where You Want to Go
It is the driver's responsibility, with advise from the on-board computer, to
choose the appropriate set of guideways to minimize the number of hops to get
to their destination.
A central computer cluster will talk to the guideways and to the cars. It will
keep track of how many cars are on each guideway, as well as their intended
route. With this information, it will advise each driver of the optimal path
to take. The driver has the option of following the advise of the computer or
not.
This mixture of optimized flow and individual freedom will allow for the
feeling of freedom that cars possess now.
Why?
One drawback of buses and coupled trains is that the individual has very little
control over where the train stops. Suppose a train passenger suddenly
remembers the dry cleaning is ready, but the train is already moving. They
have to complete that full leg of the journey before they can backtrack, or
else do without.
By providing full freedom at the end of each hop of the journey, the
most choices will be maintained. The computer-optimized solution will
just be a suggestion. If most people use the recommended route,
traffic congestion will be minimized.
By keeping the traffic flow evenly distributed across the entire service
area, there will be no concentrations to cause traffic problems.
Even when you drive on the ground, there will be less traffic because
through traffic has been taken out of the mix.
|
